Perianal abscesses are painful, pus-filled infections that develop in the tissue surrounding the anus. These infections occur when bacteria enter small glands or hair follicles in the anal area, leading to localized swelling and discomfort. Understanding the prevention methods, recognizing symptoms early, and knowing available treatment options through perianal dermatology can help individuals manage this condition effectively.
Preventing Perianal Abscesses
Perianal dermatology professionals recommend maintaining proper hygiene to prevent these abscesses. Regular cleaning of the anal area with warm water and mild soap helps remove bacteria that could lead to infection. After bowel movements, gentle cleaning from front to back prevents the spread of bacteria from the anal area to other regions.
Dietary choices play a role in prevention. A high-fiber diet promotes regular, soft bowel movements that reduce strain during defecation. Adequate water intake supports digestive health and helps maintain soft stool consistency. Foods rich in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
Managing underlying health conditions can reduce the risk of abscesses. Individuals with diabetes should maintain stable blood sugar levels, as elevated glucose can impair immune function and increase infection susceptibility. Those with inflammatory bowel disease or Crohn’s disease should work closely with healthcare providers to manage their conditions effectively.
Avoiding activities that may damage the anal area helps prevent bacterial entry points. This includes avoiding harsh wiping, using excessive force during bowel movements, or inserting foreign objects into the anal canal. Using soft toilet paper and avoiding scented products that may cause irritation also reduces the risk.
Exploring Symptoms
Pain represents the primary symptom of perianal abscesses. The discomfort typically begins as a dull ache and progresses to sharp, throbbing pain that worsens when sitting, coughing, or having bowel movements. The pain often intensifies over several days as the abscess grows.
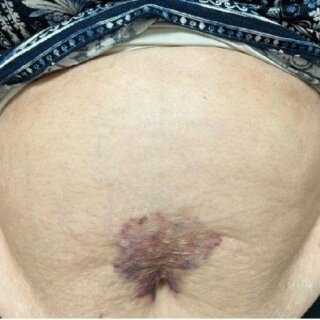
Visible swelling and redness around the anal opening indicate abscess formation. The affected area may feel warm to the touch and appear raised compared to surrounding tissue. As the infection progresses, the swelling becomes more pronounced and may develop a fluctuant or soft feeling when pressed gently.
Systemic symptoms may accompany local signs. Fever often develops as the body responds to the infection. Some individuals experience fatigue, general malaise, or chills. Difficulty sitting comfortably or walking normally may occur due to pain and swelling.
Identifying Treatment Approaches
Medical evaluation should occur promptly when perianal abscess symptoms develop. Healthcare providers can distinguish between simple abscesses and more complex conditions that may require specialized treatment. Early intervention often leads to better outcomes and reduced complications.
Surgical drainage represents the primary treatment for most perianal abscesses.
Pain management forms an integral part of treatment. Over-the-counter pain medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help manage discomfort. Prescription pain medications may be necessary for severe cases. Warm sitz baths several times daily can provide additional comfort and promote healing.
Antibiotic therapy may be prescribed in certain situations. While antibiotics alone rarely cure perianal abscesses, they may be used in conjunction with drainage for individuals with diabetes, compromised immune systems, or signs of spreading infection. The specific antibiotic chosen depends on the suspected bacterial cause.
Learn More About Perianal Dermatology
Perianal abscesses require prompt medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. While prevention strategies can reduce risk, anyone experiencing symptoms should seek healthcare evaluation rather than attempting self-treatment. Early intervention typically results in more straightforward treatment and better outcomes. If symptoms develop, contacting a healthcare provider promptly can help address the condition before complications arise.








Leave a Reply