Prostate cancer stands as one of the more frequently diagnosed cancers among men, primarily affecting individuals as they age. Though a serious condition, advancements in medical research and treatment approaches have significantly improved management strategies. Understanding the basics of prostate cancer and available treatment options can help guide conversations with medical professionals.
What Is Prostate Cancer?
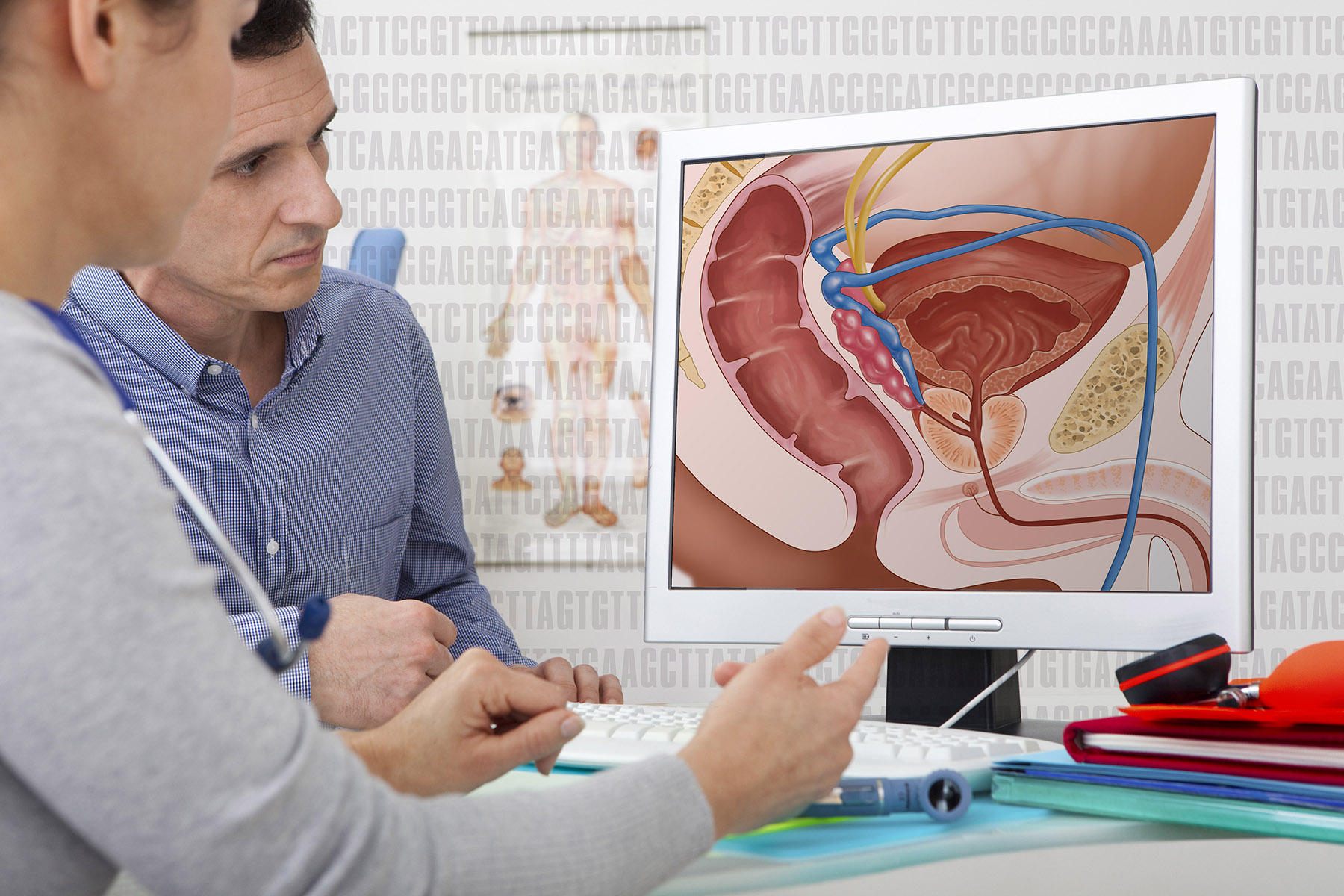
Prostate cancer occurs when cells within the prostate gland grow uncontrollably. The prostate, a small gland below the bladder in men, plays a role in producing seminal fluid. Symptoms of this cancer generally do not appear in the early stages. When symptoms do occur, they may include difficulty urinating, discomfort in the pelvic area, and blood in semen. Since these symptoms may overlap with less serious conditions like an enlarged prostate, it is necessary to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation.
Who Can Get It?
Prostate cancer primarily affects men, with age being a significant risk factor. It more commonly develops in men over the age of 50, and the likelihood increases with each subsequent decade. Men with close relatives who have been diagnosed face an elevated risk. Certain populations, such as African American men, are statistically more likely to develop the condition.
Diagnosing cancer involves several steps. A medical professional may begin with a digital rectal exam to detect abnormalities in the size or shape of the prostate. Another common test is the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) blood test, which measures levels of a protein produced by the prostate. Elevated PSA levels could signal prostate cancer, but may also result from other non-cancerous prostate conditions. If initial findings indicate the need for further investigation, imaging tests such as an ultrasound may help provide a clearer picture. A biopsy involves the removal of small prostate tissue samples. It is often conducted to confirm the presence of cancerous cells and determine the cancer’s aggressiveness.
How Is It Treated?
Treating prostate cancer depends on various factors. Such factors can include the stage of the cancer, the patient’s health, and how quickly or slowly the cancer is progressing. There are several approaches, each with specific methods tailored to the diagnosis:
- Active Surveillance: This approach is often an option for low-risk cases where the cancer grows so slowly that immediate treatment may not be necessary. Patients are closely monitored with regular PSA tests, exams, and occasional biopsies to track any changes.
- Surgery: For cases where cancer has not spread beyond the prostate, surgery may be chosen to remove the prostate gland. Known as a prostatectomy, this procedure can often lead to favorable outcomes.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy employs high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. It can be delivered externally using beams directed at the prostate or internally through brachytherapy, which involves placing radioactive seeds inside the prostate gland.
- Chemotherapy: For cancers that have spread beyond the prostate or to manage more advanced stages, chemotherapy may be recommended. This treatment uses drugs to kill rapidly dividing cells, targeting cancerous growths throughout the body.
Each treatment has its own benefits and potential side effects, and decisions about care should always involve a thorough discussion with a medical team.
Speak With a Urologist
Prostate cancer is a complex condition that requires careful management and the guidance of specialized healthcare professionals. Early detection and a tailored treatment plan can significantly impact outcomes. If you or someone you know may be experiencing symptoms or have concerns about risk factors, scheduling a consultation with a urologist is a proactive step.








Leave a Reply