Wounds are a common occurrence, whether from accidents or minor injuries during routine activities. Most wounds heal on their own. Some may require professional medical wound care to prevent complications.
What Is Wound Care?
Wound care refers to the methods and practices used to promote healing, prevent infection, and minimize scarring after an injury. Proper wound care involves cleaning the affected area, protecting it from further harm, and supporting the natural healing process. This process varies depending on the type, size, and location of the injury.
The primary goal is to create a clean environment that encourages new tissue growth. Minor cuts, scrapes, and abrasions usually require basic first aid, such as cleaning the wound with water and covering it with a sterile bandage. More severe or complex wounds may involve additional steps, such as applying specific dressings, removing dead tissue, or managing ongoing symptoms. Wound care is particularly necessary for individuals with certain chronic conditions, such as diabetes or poor circulation, as these conditions interfere with natural healing.
When Should You See a Doctor?
While many injuries are manageable at home, certain conditions signal the need for professional medical attention. Knowing what to watch for can help you determine when more advanced care is required. Below are some specific scenarios that may indicate the need for a doctor’s evaluation:
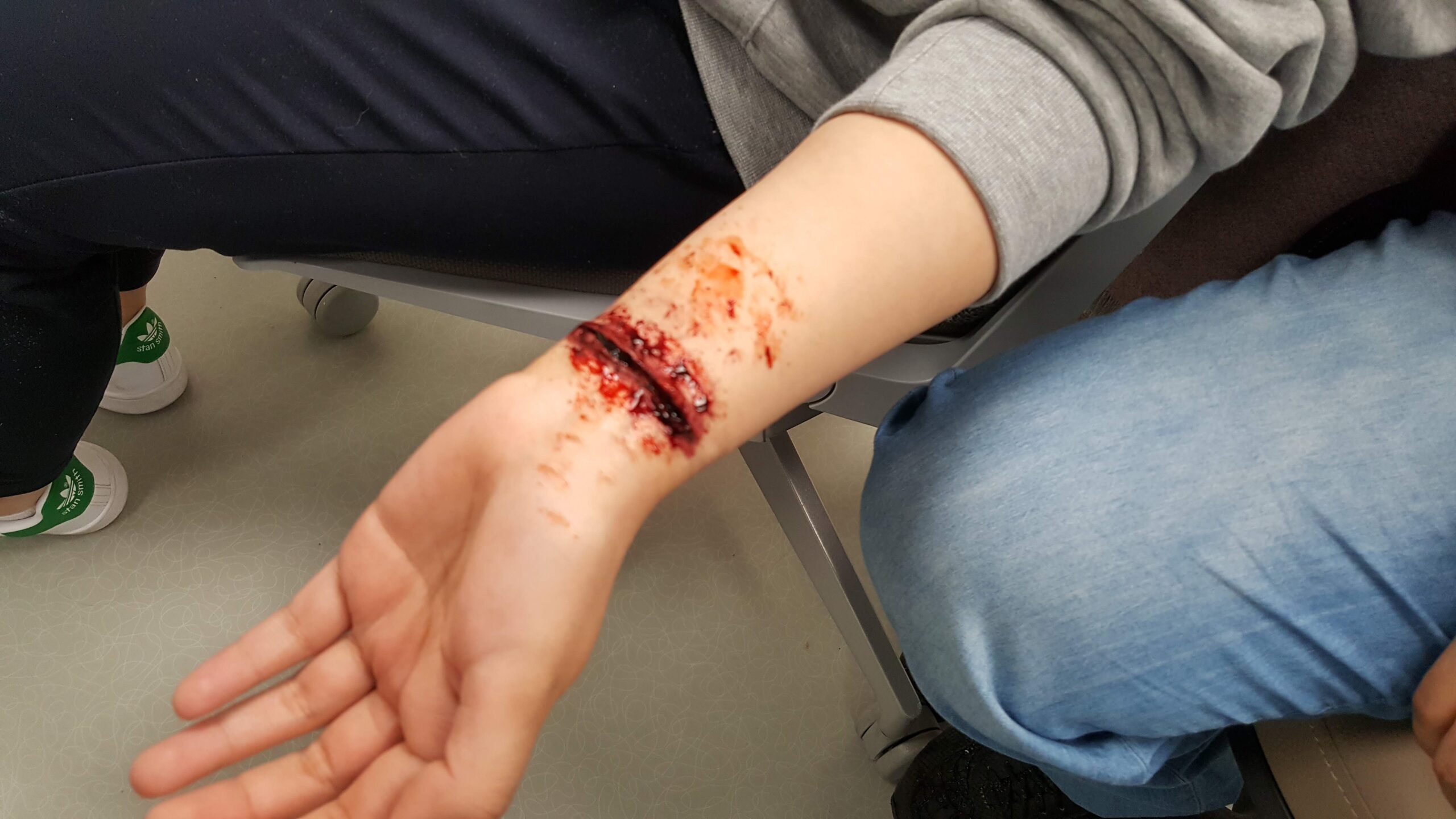
- Severe Bleeding: If bleeding does not stop after applying firm pressure for a prolonged amount of time or the wound appears to spurt blood, it may involve a damaged artery or vein. Prompt medical attention is necessary to control the bleeding.
- Signs of Infection: Redness, warmth, swelling, or pus around the wound may suggest an infection. Other signs, such as fever or chills, also indicate the need for professional care.
- Depth and Size of the Wound: Deep wounds or injuries that expose deeper tissue often require stitches or surgical intervention.
- Healing Difficulties: Wounds that do not show signs of improvement or that reopen frequently despite proper care may benefit from medical evaluation.
Being observant of these factors can guide you toward seeking timely care, facilitating better outcomes for more severe injuries.
What Does Medical Care Entail?
Medical care for wounds varies based on the nature and complexity of the injury. Professional care minimizes risks and accelerates recovery, particularly in situations where the body may not heal optimally on its own. Below are some common steps healthcare providers take when treating wounds:
- Assessment: The initial step involves a thorough evaluation of the wound. Doctors assess its size, depth, location, and risk of complications, such as infections or tissue damage.
- Cleaning: The wound is cleaned with specialized solutions to remove debris and bacteria.
- Closing the Wound: For deep or gaping wounds, stitches, staples, or adhesive strips may be used to bring the edges together and encourage faster recovery.
- Medication Application: Depending on the wound type, doctors may apply topical antibiotics, dressings, or other medications designed to prevent infection.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: For complex wounds, care often includes scheduled check-ups to monitor progress, replace dressings, and provide additional treatments if needed, such as draining fluids or prescribing antibiotics.
Seek Professional Care for Wounds
Understanding when and why to seek medical attention for wounds can empower you to take better care of yourself and those around you. While minor injuries often heal with basic first aid, certain conditions require prompt evaluation by a healthcare provider. Professional care not only addresses the immediate injury but also provides strategies for long-term healing and prevention.








Leave a Reply